Introduction
Decentralization has become a buzzword in recent years, and for good reason. It represents a fundamental shift in the way we organize and govern societies, businesses, and technologies. This concept has gained traction across various fields, from finance to technology, as it offers a promising vision of a more inclusive, resilient, and transparent world. In this article, we will explore what decentralization is, its key principles, and its profound implications for our future.
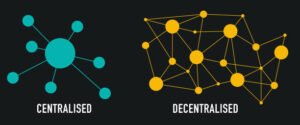
Understanding Decentralization
Decentralization, in its essence, is the redistribution of power, control, and decision-making from a centralized authority or entity to a distributed network of participants. It can be applied to various domains, such as governance, finance, technology, and more. The primary goal is to reduce dependency on single points of failure, foster inclusivity, enhance transparency, and increase resilience.
Key Principles of Decentralization
- Distributed Networks: Decentralization relies on distributed networks of participants, rather than a single central authority. This can be seen in blockchain technology, where a network of nodes verifies transactions, eliminating the need for a central authority like a bank.
- Transparency: Decentralized systems aim to be more transparent, as information is often available to all participants. In a decentralized governance model, decisions and actions are often recorded on public ledgers for anyone to review.
- Autonomy: Participants in a decentralized system have greater autonomy and control over their assets or governance. In cryptocurrencies, individuals control their private keys, providing ownership and control over their digital assets.
- Resilience: Decentralized systems are inherently more resilient to failures and attacks. Even if a part of the network fails, the rest can continue to function, ensuring continuous operation.
- Inclusivity: Decentralization aims to be more inclusive by allowing anyone to participate in the network, regardless of their geographical location or financial status. This inclusivity can democratize access to resources and opportunities.
Implications of Decentralization
- Financial Freedom: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have revolutionized the way we think about money. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offer users the ability to borrow, lend, trade, and invest without relying on traditional financial intermediaries.
- Democratized Governance: Decentralized governance models, such as DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations), enable individuals to have a say in decision-making processes, particularly in blockchain-based projects. This shift can lead to more democratic and fair governance structures.
- Privacy and Security: Decentralized technologies enhance privacy and security. Blockchain’s cryptographic principles make it difficult for unauthorized parties to access or alter data, protecting user information and assets.
- Innovation and Collaboration: Decentralization fosters innovation by allowing developers to build on open platforms and protocols. Collaboration across borders becomes easier, leading to the creation of new technologies and solutions.
- Reduced Monopoly Power: In centralized systems, a few powerful entities often dominate markets. Decentralization can break these monopolies, leveling the playing field for smaller businesses and startups.
Challenges and Considerations
While decentralization offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and considerations. These include scalability issues, regulatory concerns, energy consumption in some blockchain networks, and the need for strong security practices to protect assets.
Conclusion
Decentralization is more than just a trend; it’s a paradigm shift that has the potential to redefine how we govern, transact, and interact with technology. As the world continues to grapple with issues like inequality, data breaches, and censorship, decentralized systems offer a path forward towards a more equitable, secure, and transparent future. While challenges persist, the promise of decentralization is too compelling to ignore, and its continued development will shape the world for years to come. Embracing this evolution is not only a matter of technological progress but a statement about the values we hold in an increasingly interconnected world.